POROSITY, ITS CLASSIFICATION ON THE BASIS OF ITS PROCESSES OF FORMATION
POROSITY:-
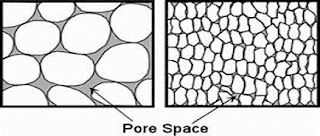
Porosity is a measure of void space in a material and is a fraction of a volume of void space over the total volume of rock.
Total Porosity= (Vv/Vt)*100TYPES OF POROSITY IN SEDIMENTARY:-
1) EFFECTIVE POROSITY
The void space in rock arranged in such a way that the pores are interconnected with each other then that type is called effective porosity.2) NON-CONNECTED/ INEFFECTIVE POROSITY
When the pore space is isolated or is not interconnected to any other pores through which a passage of liquid can’t result, but it is counted in total the porosity of rock known as ineffective porosity.
CLASSIFICATION OF POROSITY ON THE BASIS OF DEPOSITION AND DIAGENETIC HISTORY OF ROCK:-
1. PRIMARY POROSITY
2. SECONDARY POROSITY
1. PRIMARY POROSITY
The pores which are developed during the deposition of sediments, in sandstone, there is a very high porosity during the deposition stage but after further maturation porosity normally decreases and this decrease in primary porosity relates two major factors compression and lithification. For any sandstone, the depositional porosity is 35% to 40%......
Primary porosity is of two types:-
-Interparticle porosity:- The void space between sediments due to incompletely cementation of sediments is known as interparticle or intergranular porosity. Mostly the world's groundwater supply occurs in this type of pores space.


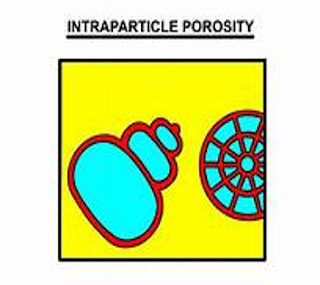
-Intra particle porosity:- The porosity which is developed due to the deposition of a hard part of an organism with sediments.
2. SECONDARY POROSITY
The void space
which develops after the deposition of sediments, during the diagenetic history of
rock. The secondary porosity of the sedimentary rock remains constant till sub mature stage, reaching to the mature
stage a sudden increase in porosity results during diagenesis.
This sudden increase in porosity after reaching a mature stage occurs
due to decarboxylation. As we know some sedimentary rocks normally have
carbonate/calcareous cement, these cement also get mature during diagenesis and start to release carbon dioxide (CO2). This released CO2 when dissolved in
water, makes the water acidic and this acidic water starts leaching
carbonaceous cement which is present in a rock (carbonate rock). This leaching
cause to develop void space referred to as secondary porosity.
Secondary porosity is of five types:-
-Inter crystalline porosity:- Rarely found porosity, mainly in igneous rock and
evaporates. The recrystallization and complete crystallization of rock develop
intercrystalline porosity. it has a planer fabric.
-Fenestral porosity:- This porosity develops in lacustrine carbonate
sediment inhomogeneous mud, Fenestral porosity
develops due to decay of organic matter and escape of gas leaving behind the
void spaces. (Pores are larger than the grain size). Pores size is more than the grain size of the rock.
-Mouldic porosity:- Many carbonate rock is made of orthochemical and allochemical constituent.
Common allochemical constituents are Ooid, peloid, bioclast, intraclast, etc. whereas orthochemical constituent includes micrites and sperits. The pores
are developed due to the dissolution of allochemical constituent because of instability at a certain rate of
diagenesis. (Pores are formed by selective removal of an individual constituent
of the rock)
qIf orthochemical constituent Ooid undergoes
dissolution then the developed porosity is called Oomouldic porosity.
Whereas
porosity due to the dissolution of peloid is known as pelmouldic porosity.
And if an orthochemical constituent
like bioclast undergoes dissolution then is called biomouldic porosity.
Only a single type of
dissolution occurs a time.
-Vuggy/Cavernous porosity:- The porosity develops due to the dissolution of
so many allochemical constituents at the same time resulting larger pores
and are not fabric selective. This type of porosity is called cavernous or vuggy porosity.
-Fracture porosity:- A type of secondary porosity produced by the tectonic the fracturing of rock due to any tectonic disturbance or an overburden
pressure release, landslide, slumping, shear fracture called as a fracture
porosity.
These fracture increases the pores space in sedimentary rocks unless it is healed or filled subsequently.
These fracture increases the pores space in sedimentary rocks unless it is healed or filled subsequently.








Comments
Post a Comment